
Mutual Funds are constituted as a trust in India. A mutual fund is the most suitable investment instrument for common savers or investors as it offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed portfolio of securities at a relatively lower cost
What are Mutual Funds?
A mutual fund is a financial instrument that pools the savings of several investors and may invest them in different financial securities like stocks, bonds, debentures, money market instruments and Government Securities, etc. or a combination of these. These securities are professionally managed by a fund manager on behalf of the unitholders and each investor holds a pro-rata share of the portfolio, that is, entitled to profits as well as losses. Each investor in a mutual fund scheme owns units of the fund, which represents a portion of his holdings of that mutual fund scheme. Profits made or income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realized is shared by the scheme unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by each one of them.
Understanding what are mutual funds with an example.
Anupam invests Rs 100,000 in a mutual fund scheme. If the price of a unit of the scheme is Rs 10, then the mutual fund house will allot him 10,000 units. A unit represents percentage ownership of the total pool of money managed in the scheme. Mutual fund units are priced at Rs 10 at the time of launch of the scheme during the new fund offer or NFO and its price fluctuates with change in the value of the underlying assets held in the scheme portfolio post-closure of equity and bond markets daily.
Let us assume the total money invested in the mutual fund scheme by all the investors including Anupam is Rs 100 Crores. The mutual fund scheme invests the money to buy stocks and other securities as mandated in the scheme offer document. Then, each unit will represent 0.000001% of all the stocks and securities that the mutual fund scheme has in its portfolio. As Anupam has 10,000 units, then his portion of the mutual fund unit holdings will be 0.01%. As the value of securities held by the scheme in its portfolio increases or decreases, so will the price of the units (NAV). For example - If the total value of holdings increases from Rs 100 Crores to Rs 120 Crores assuming no new units have been issued, the per-unit price or NAV will be Rs 12 (0.000001% X 120 Crores). Please note that the percentage ownership of the units of the scheme represented by Anupam and other unitholders will change from time to time as new investors may invest in the scheme and/or existing investors may redeem from it.
How do mutual funds work in India?
The Mutual funds are set up as a trust and the following is the structure of a typical Mutual fund
Sponsor
The sponsor is the corporate body, which establishes a mutual fund. The sponsor must contribute at least 40% of the net worth of the investment managed and meet the eligibility criteria prescribed under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)Mutual Funds Regulations, 1996. The sponsor is not responsible or liable for any loss or shortfall resulting from the operation of the schemes beyond the initial contribution made by it towards setting up of the mutual fund Trust
Trust
The mutual fund is constituted as a trust per the provisions of the Indian Trusts Act, 1882 by the sponsor. The trust deed is registered under the Indian Registration Act, 1908.
Trustee
The trustee is usually a company (corporate body) or a Board of Trustees (body of individuals). The main responsibility of the trustee is to safeguard the interest of the unitholders. Trustees ensure that the Asset Management Company (AMC) functions always in the interest of the investors of the schemes and in accordance with the various guidelines given by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the provisions of the trust deed, and the offer documents of the respective schemes. At least 2/3rd of the directors of the Trustee should be independent directors who are not associated with the sponsor in any manner whatsoever.
Asset Management Company (AMC)
The trustee, as the investment manager of the mutual fund, appoints the Asset Management Company or the AMC. The AMC is required to be approved by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to act as an asset management company of the Mutual fund. At least 50% of the directors of the AMC should be independent directors who are not associated with the sponsor in any manner whatsoever. The AMC must have a net worth of at least Rs. 50 Crore at all times. The required net worth was earlier Rs 10 Crores but the same was revised to Rs 50 Crores by SEBI in February 2014. All the AMCs were given 3 years to adhere to this.
Custodian
Custodians are a trusted company, bank, or similar financial institution that is registered with SEBI and is responsible for holding and safeguarding the securities owned within a mutual fund.
Registrar and Transfer Agent
The AMC appoints the registrar and transfer agent (R&T) to the mutual fund schemes. The R&T agents process the application form, redemption requests and dispatches account statements to the unitholders. The R&T agents also handle communication with investors, do scheme accounting, and updates investor records.
FAQs
- Can you lose money in a mutual fund?
All Mutual funds come with a disclaimer that says “Mutual funds are subject to risk.” So, one can lose money in mutual funds, hence, should focus on long-term mutual funds. - What is a mutual fund in simple terms?
Mutual funds are small investment plans that are managed by Asset Management Companies. It pools small investments and collectively invests in the stock market. - What are the 3 types of mutual funds?
The three types of mutual funds are
- Money Market Funds
- Bond Funds
- Stock Funds
- What are the pros and cons of investing in mutual funds?
Few of the pros and cons of investing in mutual funds are
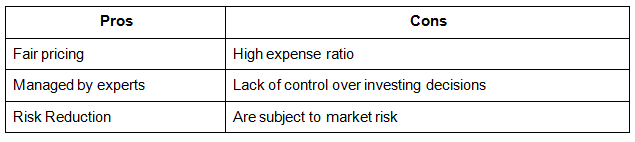
- How do beginners invest in mutual funds?
As a beginner, one should invest in SIPs or long-term mutual funds. They should not go more big amounts like 10,000 etc, rather start with a minimal investment of Rs 500.
Conclusion
Despite the risk involved in Mutual funds, it is a popular mode of investment in India. Mutual funds are managed by AMCs, but one should not completely rely on AMCs and do comprehensive research on Mutual funds before investing. People should decide beforehand about what type of mutual fund they want to invest in and why.