
Mutual funds in India can be categorized into various types depending on their structures, underlying investments, tax treatment, nature of the scheme management, and various investor goals. Based on these parameters there can be two types of mutual funds:-
Primary Classification of Mutual Funds
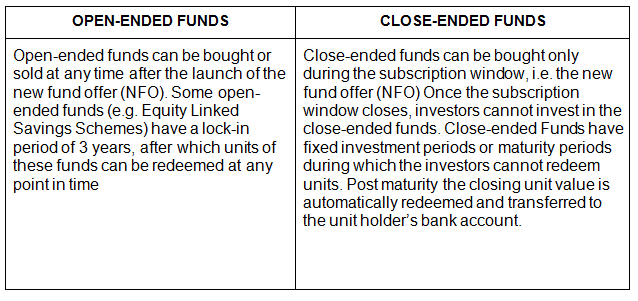
Note: Some close-ended funds can become open-ended funds after the maturity date or the AMC might give the option to roll over the redemption proceeds to some other fund.
Based on the Investment
Based on the underlying investments in open and closed-ended funds, broadly there are 4 different types of mutual funds in India. But before that, let us see what are Mutual Funds in India
- Equity Mutual Funds: Equity mutual funds seek to invest their corpus in equity and equity-related securities. Equity funds can further be categorized into large-cap funds, diversified or multi-cap funds, and mid and small-cap funds. Large-cap funds invest most of the investments in large-cap companies, midcap funds invest mostly in shares of small-cap and mid-cap companies, while multi-cap funds (also known as Flexi-cap or diversified equity funds) have substantial exposures to both large-cap and midcap stocks and also across various sectors of the economy.
The majority of mutual fund schemes (whether large-cap, diversified, or mid and small-cap) invests across many sectors and therefore can be called diversified equity schemes. Some mutual fund schemes, however, may invest in particular sectors (e.g. banking, FMCG, pharma, technology, infrastructure, automobile or entertainment, etc.). These funds are called sector funds and therefore, they are not diversified equity funds.
See how the top-performing funds performed historically - Debt Funds: Debt funds seek to invest their corpus in money market and / or debt market securities. Money market securities include commercial papers, certificates of deposits (CDs), treasury bills, etc. Debt market securities include government bonds, PSU bonds, non-convertible debentures, etc.
Debt funds can be further categorized into sub-categories depending based on the maturities or duration of the underlying securities in the scheme portfolio. Liquid funds invest in money market securities whose residual maturities are usually less than 90 days. Ultra-short term debt funds invest in money market securities whose residual maturities are in the range of 90 days to a year. Short term debt funds invest in debt securities whose maximum duration is 2 – 3 years, while long term debt funds (popularly known as income funds) invest in debt securities with longer durations. - Hybrid mutual funds: Hybrid funds invest in both equities as well as debt instruments. The percentage allocation to equity and debt depends on the asset allocation mandates of the respective schemes. There are two types of hybrid funds – equity-oriented hybrid funds (popularly known as balanced funds) and debt-oriented hybrid funds (popularly known as MIPs). Balanced Funds have at least 65% exposure to equities and balance to debt securities whereas debt-oriented hybrid funds or MIPs have majority exposure to debt.
- Tax Saving mutual funds: Tax Saver Funds are also known as Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), or tax saver funds or ELSS funds, which are a type of equity funds, which enjoy Section 80C tax saving benefit. Investment of up to Rs 1.5 lakhs in ELSS Funds can be deducted from the investor’s taxable income for income tax computation under Section 80C of The Income Tax Act 1961
From the Taxation Perspective
We have seen are different types of mutual funds in India, however, from a tax perspective, there are only two types of mutual funds in India – equity funds and non-equity funds.
Equity funds have at least 65% exposure to equity or equity-related securities, whereas non-equity funds have less than 65% exposure to equity. Equity funds enjoy equity tax benefits; the tax treatment of non-equity funds is different from equity funds.
Situation specific Mutual funds
There are mutual funds schemes in India that aim to provide solutions to specific investor goals like retirement planning, children’s higher education or marriage, asset allocation, dynamic funds, etc. Examples of these types of funds are retirement plans, children plans, asset allocation funds, dynamic funds, and life stage funds, etc.
People Often Ask
- Which type of mutual funds are best?
Different types of Mutual funds are best for different purposes but based on popularity, these are the mutual funds that people prefer
- Equity or growth schemes
- Liquid funds
- Debt Mutual Funds
- Balanced Funds
- Which is better FD or MF?
In Fixed Deposit (FD) the rate of interest is fixed whereas in a Mutual fund the rate of interest changes as per the market. Therefore, it is better to invest in mutual funds for long term investment as they give better returns. - Can my mutual fund go to zero?
In a hypothetical situation, yes the value of a mutual fund can go to zero. The value of a mutual fund does fluctuate depending on the type of mutual fund and the market conditions. - What happens to mutual funds if the market crashes?
When the market crashes, the Net Value of Asset (NAV) or the price of the mutual fund also decreases. So, one should refrain from taking money out of the mutual funds.
Conclusion
Mutual funds provide customized solutions to a variety of investment goals and have many benefits. So, one can select mutual funds based on their need and requirement.